Study area and period
The study was carried out at Haramaya University, College of Health and Medical Sciences (HUCHMS) from July 01 to August 30, 2022. Haramaya University was established in 1954 next to Addis Ababa University in Ethiopia. It is located approximately 510 km away from Addis Ababa in the Oromia National Regional State, East Hararghe administrative zone. The study programs of the university range from undergraduate to postgraduate levels on its 3 campuses and 13 colleges. Among these colleges, the College of Health and Medical Science (CHMS) is one of the colleges that was established in September 1996 with the objective of training health professionals who contribute to filling the health needs of the country. The CHMS is organized for the School of Medicine, School of Pharmacy, School of Nursing and Midwifery, School of Medical Laboratory Science, School of Public Health and Environmental Health Department. Currently, 1754 students are enrolled in undergraduate and postbasic programmes at the college (source: CHMS registrar office).
Study design, period and population
An institutional-based cross-sectional study was conducted. The source population was all students in the faculty of health and medical sciences affiliated with clinical attachment, and all students selected from each department at HUCHMS with clinical attachment composed the sample population. All undergraduate clinically affiliated students from the selected department at the CHMS were recruited. Patients who had nasal infections, nose bleeding during the study period, or who received intranasal antibiotic ointment or other antibiotics within the previous two weeks of the commencement of the study were excluded. The source population for this study comprised all undergraduate students enrolled during the study period at Haramaya University’s CHMS. On the other hand, all of the selected students from each department were considered the study population during the study period.
Sample size determination and sampling technique
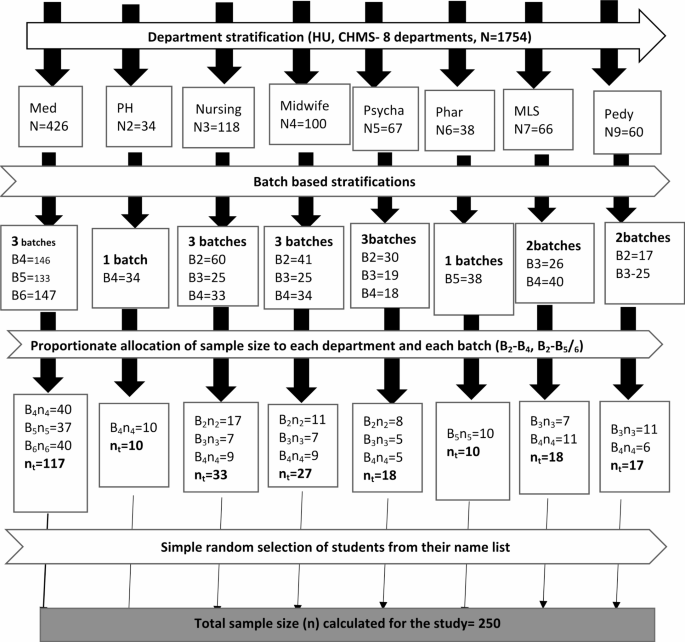
The sample size was determined by a single population proportion formula using the prevalence of nasal carriage of S. aureusfrom a study conducted at Arbaminch University and was 27.1%9, with a Z score for a 95% confidence interval of 1.96 and a margin of error of 5%. Since there is a small population of students with clinical attachment at the campus (N = 909), a reduction formula was used, and a 10% nonresponse rate was added. The final sample size was 250. Then, this sample size was allocated proportionally to each department and then batches within the departments. Health and medical sciences students were stratified based on academic year; the final sample size was allocated proportionally to each academic year during the study period. A simple random sampling technique was used to select participants who fulfilled the inclusion criteria from each departmental batch by using a student roster as a sampling frame that was collected from each department. Finally, a simple random sampling technique was used to select the participants. The randomness of the sample was ensured by using a lottery method (Fig. 1).
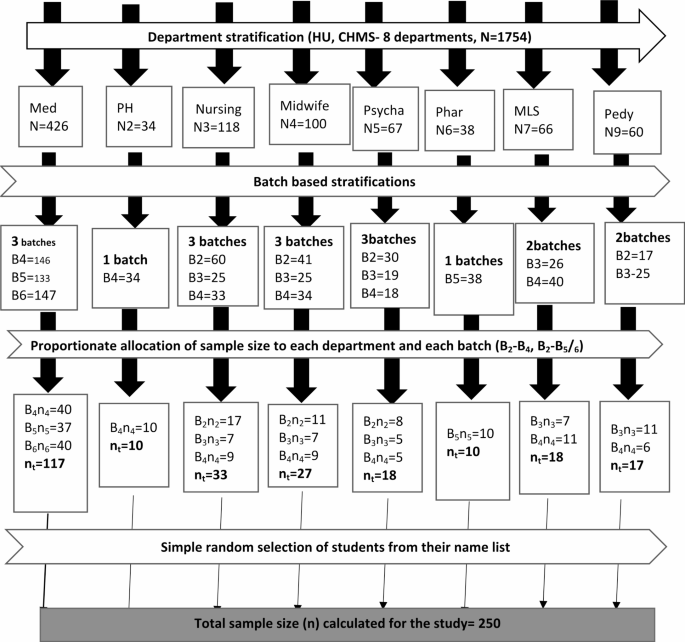
Source: CHMS, Registrar office.
A flow diagram illustrating sampling procedure to recruit participants among clinically affiliated students at Haramaya University, college of health and medical sciences, Harar, Eastern Ethiopia, 2022 (n = 250). Key: Med: Medicine, PH: Public Health, Psycha: Psychiatry, Pharma: Pharmacy, MLS: Medical Laboratory Sciences, Pedy: Pediatrics.
Data collection and laboratory investigations
A structured questionnaire developed from different types of literature was used to collect the data1,6,9. The questionnaire aimed to assess sociodemographic variables, behavioral features and clinical information. Nasal swab specimens were collected by using sterile cotton tip swabs prewetted with sterile saline for participants’ anterior nares to a depth of approximately 1 cm and rotation against the interior surface of the nostril. Then, the swabs were inserted into Amies transport medium (Oxoid, UK) and transported to the Microbiology Laboratory for investigation.
The samples were inoculated onto Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) (Oxoid Ltd. England) to confirm the fermentation of Mannitol, the growth of golden yellow colonies on MSA (Oxoid, Cambridge, UK) surrounded by yellow zones after 24 h of incubation at 37 °C indicated a positive result for S. aureus. Furthermore, isolates were sub-cultured onto Blood Agar Plate, and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Colony morphology, Gram stain reaction, and biochemical tests such as catalase, coagulase, and DNase tests test were performed to confirm S. aureus11,12.
Antibiotic susceptibility profiling of all isolates was achieved by the Kirby–Bauer disk diffusion technique. Bacterial inoculum equivalent to the opacity of 0.5 McFarland standards were prepared, swabbed over the Muller Hinton Agar (MHA) surface, exposed to antibiotic disks, and then incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. The diameters of the zones of inhibition were measured and categorized as susceptible, intermediate, or resistant according to the methods described in the CLSI13. The standard antimicrobial disks (oxoid, UK) used were penicillin (10 mg), ciprofloxacin (5 mg), clindamycin (2 mg), gentamicin (10 mg), erythromycin (15 mg), chloramphenicol (30 mg), ampicillin (10 mg), tetracycline (30 mg), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (25 mg) and cefoxitin (30 mg)13. Finally, MRSA was detected by placing 30 µg of cefoxitin per disk on Mueller-Hinton agar. The zone of inhibition was determined after 24 h of incubation at 35 °C. All isolates ≤ 24 mm of cefoxitin were considered to be MRSA14.
Data and laboratory quality control
The questionnaire was pretested (5% of the sample size or 13 sample) on health science students at other nearby universities (Diredawa University). The findings from the pretesting were utilized for modifying and adjusting the instrument. Two days of training were provided to the data collectors and supervisors on the data collection tool and the data and sample collection procedures. For daily activities, the data collectors were supervised closely by the supervisors and the principal investigator. The completeness of each questionnaire was checked by the principal investigator and the supervisors on a daily basis. Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25,923 and Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) were used as positive and negative controls, respectively, to maintain laboratory quality and investigations. All culture media were prepared according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and sterility was checked by incubating 5% of each batch of the prepared culture media at 37 °C overnight. All culture plates and antibiotic discs were stored at the recommended refrigeration temperature (2–8 °C).
Data processing and analysis
After the data were collected, each questionnaire was thoroughly reviewed for completeness and consistency by the data collectors, supervisors and principal investigators. Then, the data were coded and entered into IBM SPSS version 25 software. Every participant had a unique identification number. Descriptive statistical analysis was used to summarize the findings of the studies using frequency, mean, and proportion. The results were presented in figures, tables and text. Bivariable analysis was carried out using the chi-square test to determine potential factors associated with the MRSA carriage rate. Finally, variables with a p value less than 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.
link





More Stories
Otolaryngology (ENT)/Head and Neck Surgery – Overview
What doctors wish patients knew about which cold medicines work
Snotless nose designed to teach medical students where to stick it